Think of an AI as the world’s most talented, fastest-working intern. This intern has read almost every book ever written and can draft a report in seconds. However, there is one catch: they can’t read your mind. If you give them a vague instruction like “Write a letter,” they might write a love poem, a legal notice, or a complaint about a toaster.
The secret to getting exactly what you want from an Artificial Intelligence (AI) is called prompting. A prompt is simply the instruction or question you type into the chat box. Learning the basics of prompting is like learning a new language—once you know the “grammar” of a good prompt, the AI becomes a powerful tool that can save you hours of work every day.
The Golden Rule: Specificity is King
If you remember only one thing from this guide, let it be this: Be specific. Vague prompts lead to vague (and often useless) answers.
- Weak Prompt: “Write a healthy recipe.”
- Strong Prompt: “Write a 30-minute vegetarian dinner recipe for a family of four. Avoid using nuts, and make sure the instructions are easy for a beginner cook to follow.”
Notice how the second prompt gives the AI “guardrails.” It tells the AI the time limit, the dietary needs, the audience size, and the skill level. By narrowing the focus, you ensure the result is actually something you can use.
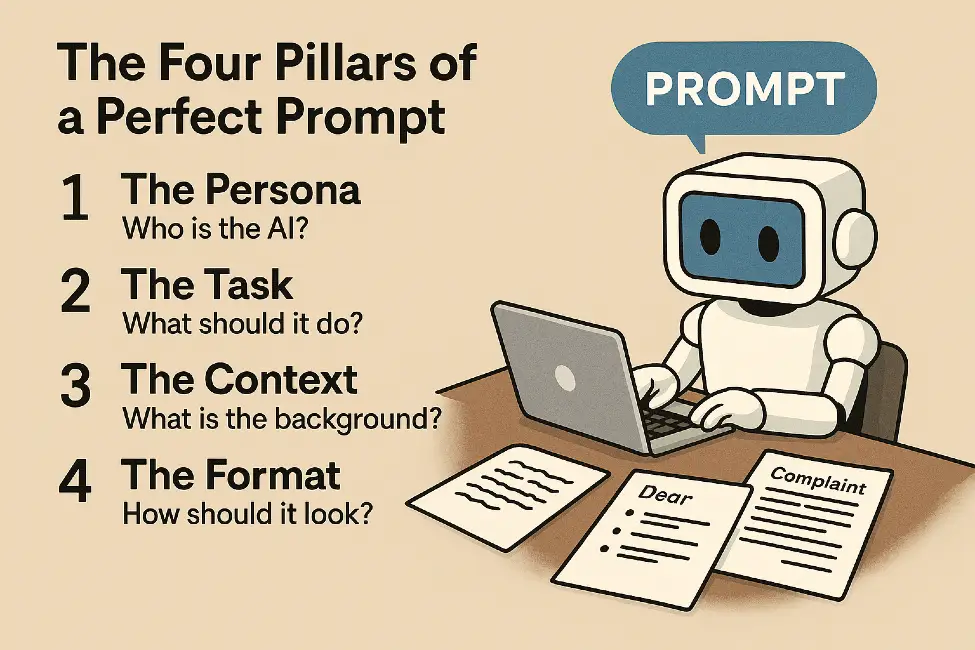
The Four Pillars of a Perfect Prompt
To consistently get high-quality results, try to include these four elements in your prompts. You don’t need all of them every time, but the more you include, the better the output will be.
1. The Persona (Who is the AI?)
Tell the AI who it should pretend to be. Assigning a role changes the tone and the expertise level of the response.
- Example: “You are a world-class travel agent…” or “You are a professional editor with a knack for making writing more punchy.”
2. The Task (What should it do?)
Use a clear action verb to describe exactly what you want.
- Example: “Summarize this article,” “Create a list,” “Draft an email,” or “Debug this code.”
3. The Context (What is the background?)
Give the AI the “why” and the “who.” Who is the audience? What is the goal? What constraints exist?
- Example: “I am writing to a busy CEO who only has one minute to read this. Keep the tone formal and use three bullet points for the main ideas.”
4. The Format (How should it look?)
Tell the AI how to structure the information. Do you want a table? A list? A poem? A JSON code block?
- Example: “Format your response as a table with columns for ‘Pros,’ ‘Cons,’ and ‘Cost Estimate.’”
Essential Prompting Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the four pillars, you can use these “pro” techniques to fine-tune your results.
Zero-Shot vs. Few-Shot Prompting
- Zero-Shot: You ask a question with no examples. (e.g., “Translate ‘Hello’ to French.”)
- Few-Shot: You give the AI a few examples of what you want first. This is incredibly helpful for teaching the AI a specific style or format.
- Example: “I want to turn names into initials. John Doe -> J.D. Jane Smith -> J.S. Now do: Robert Brown.”
Chain of Thought (Think Step-by-Step)
For complex problems, especially math or logic, ask the AI to “think step-by-step.” This simple phrase forces the AI to break the problem into smaller pieces, which significantly reduces errors.
Constraints (The Power of “No”)
Sometimes telling the AI what not to do is as important as telling it what to do.
- Example: “Explain how a car engine works. Do not use any technical jargon and keep it under 100 words.”
Common Prompting Mistakes to Avoid
| Mistake | Why it fails | The Fix |
| The “Wall of Text” | Too much information at once confuses the AI. | Break complex tasks into smaller, separate prompts. |
| Assuming Knowledge | AI doesn’t know your company’s internal slang or your personal history. | Provide the necessary background info within the prompt. |
| One and Done | Expecting the first answer to be perfect. | Treat it like a conversation. Ask for edits and refinements. |
| Being Too Polite | Adding “Please” and “Thank you” is nice, but it doesn’t improve the AI’s logic. | Focus on clarity and direct instructions. |
The “Secret Sauce”: Iteration
The best prompt engineers aren’t people who write one perfect sentence. They are people who iterate. If the AI gives you an answer that is “almost right,” don’t start over. Just talk to it.
“I like the email you wrote, but it sounds a bit too aggressive. Can you make the tone more friendly and add a sentence thanking them for their time?”
This back-and-forth conversation is where the magic happens. You are “sculpting” the response until it fits your vision.
Conclusion
Mastering AI prompts isn’t about learning code; it’s about learning how to communicate clearly. By being specific, providing context, and treating the process as a conversation, you can turn any AI into a specialized assistant. Start small—try giving the AI a persona today and see how much the “vibe” of its answers changes.