Think of a Generative AI as the world’s most talented, fastest-working intern. This intern has processed nearly every book ever written and can draft a technical report in seconds. However, there is one catch: they can’t read your mind. If you give them a vague instruction like “Write a letter,” the output might be a love poem, a legal notice, or a complaint about a toaster.
The secret to unlocking the full potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) is called prompting. A prompt is the specific input or command you type into the interface. Learning the basics of prompt engineering is like learning a new language—once you master the “grammar” of a high-quality prompt, AI becomes an amazing tool that can save you hours of manual labor every day.
The Golden Rule: Specificity is King
If you remember only one thing from this beginner’s guide, let it be this: Be specific. Vague prompts lead to generic, hallucinated, or useless answers.
- Weak Prompt: “Write a healthy recipe.”
- Strong Prompt: “Write a 30-minute vegetarian dinner recipe for a family of four. Avoid using nuts, and ensure the instructions are simple enough for a beginner cook.”
The second prompt provides “guardrails.” By defining the time limit, dietary restrictions, audience size, and skill level, you ensure the AI generates a practical, actionable result.cus, you ensure the result is actually something you can use.
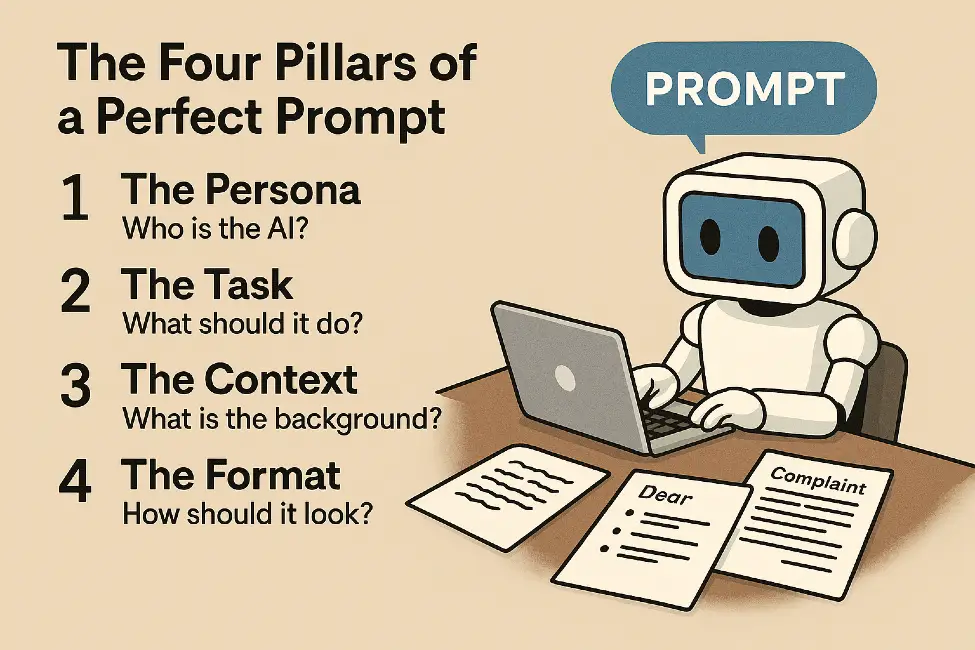
The Four Pillars of a Perfect Prompt
To get high-quality results from tools like ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini every time, include these four parts in your prompt.
1. The Persona (Assign a Role)
Tell the AI who it should pretend to be. Defining a persona shifts the tone and the expertise level of the response.
Example: “You are a world-class travel agent…” or “You are a professional editor specializing in punchy, minimalist copy.”
2. The Task (Define the Action)
Use clear, imperative verbs to describe the objective.
Example: “Summarize this transcript,” “Generate a list,” or “Debug this Python script.”
3. The Context (Provide Background)
Give the AI the “why” and the “who.” What is the goal? Who is the end-user?
Example: “I am writing to a busy CEO with a one-minute attention span. Keep the tone formal and use three bullet points for the main ideas.”
4. The Format (Structure the Output)
Specify how the information should be presented.
Example: “Format your response as a Markdown table with columns for ‘Pros,’ ‘Cons,’ and ‘Projected Cost.’”
Essential Prompting Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the pillars, use these professional techniques to fine-tune your AI-generated content.
- Zero-Shot vs. Few-Shot Prompting: * Zero-Shot is asking a question with no context (e.g., “Translate this to Spanish”).
- Few-Shot involves providing examples to teach the AI a specific style (e.g., “Input: Apple -> Output: Fruit; Input: Carrot -> Output: Vegetable; Input: Salmon -> Output: ?”).
- Chain of Thought (CoT): For complex logic or math, ask the AI to “think step-by-step.” This forces the model to break down the problem, significantly reducing reasoning errors.
- Negative Constraints: Telling the AI what not to do is vital. (e.g., “Explain quantum physics without using the word ‘particle’ and keep it under 100 words.”)
Common Prompting Mistakes to Avoid
| Mistake | Why it fails | The Fix |
| The “Wall of Text” | Overwhelming the model with data. | Break complex tasks into smaller, sequential steps. |
| Assuming Knowledge | AI lacks access to your private files/slang. | Provide all necessary background info within the chat. |
| One and Done | Expecting perfection on the first try. | Treat it as a conversation; ask for specific edits. |
| Over-Politeness | Using “Please” and “Thank you.” | Focus on clarity; being nice doesn’t improve AI logic. |
The “Secret Sauce”: Iteration
The best prompt engineers don’t just write one perfect sentence; they iterate. If the output is “almost right,” don’t start over. Provide feedback.
“I like this email, but it sounds too aggressive. Soften the tone and add a sentence thanking the recipient for their patience.”
This back-and-forth “sculpting” is where the most valuable AI insights are found.
Conclusion
Mastering AI isn’t about learning code; it’s about learning how to communicate with clarity. By providing context and treating the process as a collaborative dialogue, you can turn any LLM into a specialized virtual assistant. Start small—try giving your AI a specific persona today and watch how the quality of the “vibe” transforms.
Conclusion
Mastering AI prompts isn’t about learning code; it’s about learning how to communicate clearly. By being specific, providing context, and treating the process as a conversation, you can turn any AI into a specialized assistant. Start small—try giving the AI a persona today and see how much the “vibe” of its answers changes.